

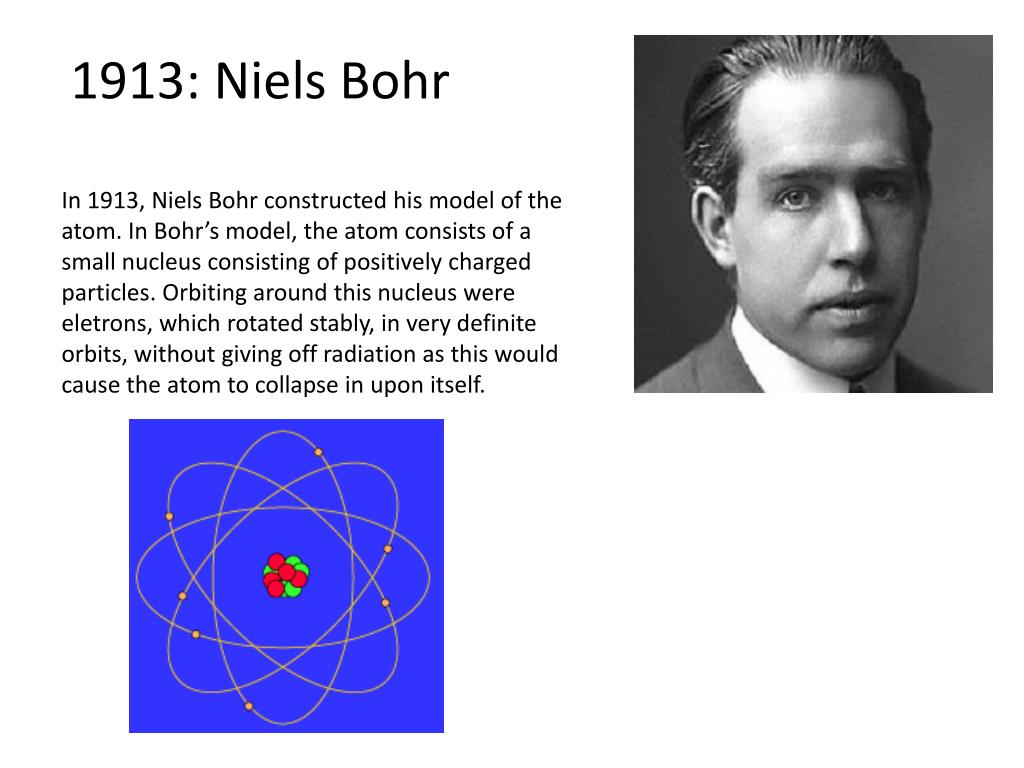
As you move up or down a ladder, you can only occupy specific rungs and cannot be in the spaces in between rungs. An everyday analogy to the Bohr model is the rungs of a ladder. The electron is not allowed to occupy any of the spaces in between the orbits. The orbits that are further from the nucleus are all of successively greater energy. The ground state of the hydrogen atom, where its energy is lowest, is when the electron is in the orbit that is closest to the nucleus. Describes Bohrs development of an atomic model capable of explaining the spectrum of hydrogen. When the electron is in one of these orbits, its energy is fixed. The Bohr atomic model: Niels Bohr Abstract.
Rutherford had shown that the atom consisted of a.

It accounts for a wide range of physical phenomena, including the existence of discrete packets of energy and matter, the uncertainty principle, and the exclusion principle.Īccording to the Bohr model, often referred to as a planetary model, the electrons encircle the nucleus of the atom in specific allowable paths called orbits. In 1913, Bohr published a theory about the structure of the atom based on an earlier theory of Rutherfords.

This is a theory based on the principle that matter and energy have the properties of both particles and waves. This was the basis for what later became known as quantum theory. When the energy is removed, the electrons return back to their ground state, emitting a corresponding amount of energy-a quantum of light, or photon. (Credit: Zachary Wilson Source: CK-12 Foundation License: CC BY-NC 3.0(opens in new window))īohr explained that electrons can be moved into different orbits with the addition of energy. Also, the value of E n becomes zero when n reaches to ∞.\): Bohr's atomic model hydrogen emission spectra. It means the value of E becomes less negative with the increase in the value of square of n. If ‘m’ is the mass of an electron revolving around the nucleus with a velocity ‘v’ in a circular orbit, then the required centripetal force is:Īlso, the electrostatic force of attraction between the nucleus of charge (+Ze) and the electron is (- e) will be:į = \ eV = - 0.3778 eV…(f)Ī pattern from eq (a) to (f) shows us that the value of E 1 n 2. For that work he received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1922. Negatively charged electron revolves about the nucleus in a circular orbit, the centripetal force required for revolution is provided by the electrostatic force of attraction between the nucleus and electrons. He was the first to apply the quantum concept, which restricts the energy of a system to certain discrete values, to the problem of atomic and molecular structure. The first postulate states that every atom has a positively charged central core called the nucleus in which the entire mass of an atom is concentrated. There are three Bohr’s Postulates in Neil Bohr Model, each of these are described in detail below: First Postulate There are three Bohr’s postulates of atomic models, we will talk about these in detail. Bohrs model of the hydrogen atom was the very first model of atomic structure that explained the spectrum of hydrogen model. To overcome this, Neil Bohr combined classical ideas with the quantum concepts of Planck to give something, which is known as the Neil Bohr atomic model of Hydrogen. Viewing the demerits of the Rutherford model, Neil Bohr concluded that classical mechanics and electromagnetism cannot be applied to the processes on the atomic scale. The transfer of electrons is possible by emission and absorption of energy. The orbits are symbolized with the letter ‘n’, where the value of n is an integer. Bohr's Model explained how electrons travel in different circular orbits around the nucleus.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
